Introduction
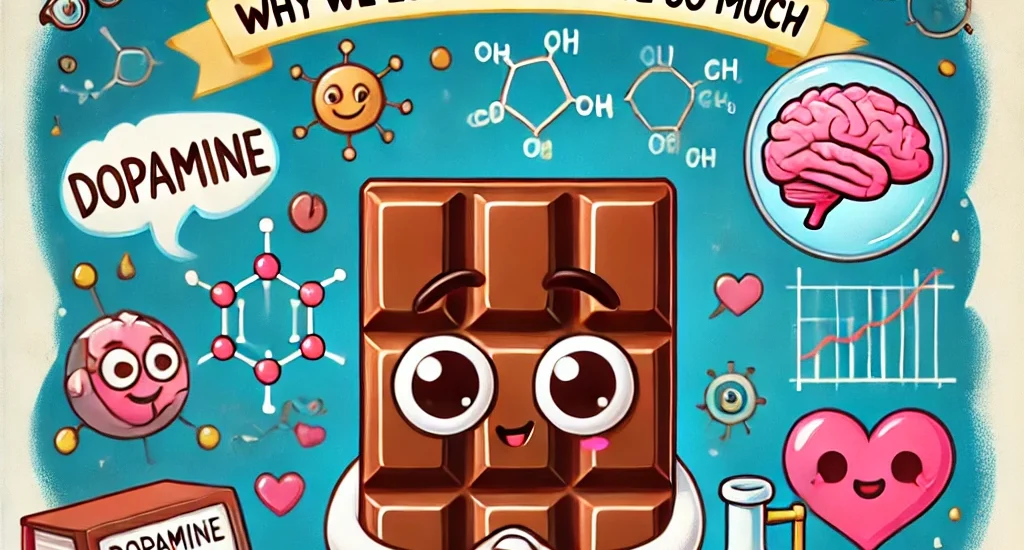
Chocolate is arguably one of the most beloved foods worldwide, often evoking intense cravings and emotional responses. But what is it about chocolate that makes it so addictive and comforting? Beyond its rich flavor and texture, chocolate contains a unique combination of chemical compounds that influence our brain chemistry, mood, and even appetite.
This article delves into the scientific explanations behind chocolate cravings, exploring the neurochemical, psychological, and sensory factors that contribute to our deep-seated love for chocolate.
1. Chemical Compounds in Chocolate That Affect the Brain
Chocolate contains several psychoactive compounds that influence mood and cravings:
- Theobromine: A mild stimulant related to caffeine, which can increase alertness.
- Caffeine: Present in small amounts, it contributes to stimulating effects.
- Phenylethylamine (PEA): A compound linked to mood elevation and feelings of love.
- Anandamide: An endogenous cannabinoid that binds to cannabinoid receptors, producing mild euphoria.
- Flavanols: Antioxidants that can improve brain function and blood flow.
Together, these compounds stimulate neurotransmitters and receptors associated with pleasure and reward.
2. The Role of Neurotransmitters in Chocolate Cravings
Chocolate consumption affects several key neurotransmitters:
Dopamine
Dopamine is the brain’s primary reward chemical. Eating chocolate triggers dopamine release, reinforcing pleasurable sensations and driving repeated cravings.
Serotonin
Serotonin regulates mood and appetite. Chocolate contains tryptophan, a serotonin precursor, which can help elevate mood and reduce stress.
Endorphins
Eating chocolate can stimulate endorphin release, the body’s natural painkillers, producing feelings of well-being and relaxation.
3. Psychological and Emotional Factors
Chocolate cravings are often linked to emotional states:
- Comfort Food: Chocolate is associated with comfort, stress relief, and reward.
- Emotional Eating: Many people consume chocolate to cope with negative emotions.
- Memory and Conditioning: Positive experiences with chocolate can condition the brain to seek it when stressed or sad.
4. Sensory Appeal of Chocolate
Chocolate’s sensory qualities—its smooth texture, rich aroma, and sweet-bitter taste—stimulate the senses in ways that enhance craving.
- Melting texture activates pleasure centers in the brain.
- Sweetness triggers innate preferences.
- Aroma compounds stimulate olfactory receptors linked to memory and emotion.
5. Hormonal Influences on Chocolate Cravings
Hormonal changes, especially in women, can influence chocolate cravings:
- Menstrual Cycle: Fluctuations in estrogen and progesterone can heighten cravings premenstrually.
- Stress Hormones: Cortisol can increase appetite for high-calorie comfort foods like chocolate.
6. Chocolate Addiction: Myth or Reality?
While chocolate cravings are real, the idea of chocolate as an addictive substance is debated:
- Some researchers argue chocolate can produce mild dependence-like symptoms.
- However, chocolate addiction lacks many criteria of substance addiction, such as severe withdrawal or compulsive use.
- More research is needed to understand chocolate’s addictive potential fully.
7. Managing Chocolate Cravings
For those seeking to manage cravings, strategies include:
- Eating small amounts mindfully to satisfy cravings without overindulgence.
- Replacing chocolate with healthier alternatives like nuts or fruit.
- Addressing emotional triggers through stress management and counseling.
- Staying hydrated and maintaining balanced nutrition.
Conclusion
Chocolate cravings are the result of a complex interplay between chemistry, psychology, and sensory pleasure. Understanding the science behind these cravings can help us enjoy chocolate in a balanced way and appreciate the remarkable ways this ancient food interacts with our brain and emotions.
Whether it’s a moment of comfort or a burst of happiness, chocolate continues to captivate our senses and hearts worldwide.
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4696435/
- https://www.psychologytoday.com/us/blog/brain-food/201612/the-science-behind-chocolate-cravings
- https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/chocolate-cravings
- https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2021.644704/full
- https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2020/02/200211101732.htm